Neuralink: brain-computer interface technologies and its implications
The interest in the implementation of systems that could establish direct communication with the human brain has grown to such an extent that to date applications have been proposed for the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of a wide variety of diseases with neurophysiological and neuropsychological affectation.
Some relevant proposals have been the detection of levels of consciousness in patients in coma, vegetative state or state of minimal consciousness, the increase of attention levels in children with hyperactivity disorders and attention deficits, the cognitive and affective regulation of people with schizophrenia or epilepsy, the improvement of social interaction of children with autism and the ability to feel people wearing prostheses or paraplegic people.
How do Brain-Computer Interfaces work?
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) record the neural activity of the Central Nervous System, and then produce outputs that replace, restore, increase, supplement or improve the natural outputs of such systems. Therefore, the interaction between the human beings and their internal or external environment is transformed. Some medical examples are controlling devices such as prostheses or wheelchairs, allowing people who have lost the ability to care for themselves to regain their independence.
A BCIs converts a user's intentions (control task) encoded in a specific neural mechanism into actual actions in six fundamental phases:
Brain activity is acquired which is achieved through various recording techniques that are grouped into three categories based on the type of brain activity they capture: electrical, chemical or metabolic. Each of the techniques has characteristics that make them suitable according to the information we wish to obtain.
The information acquired is processed with the main objective of eliminating both internal and external artifacts.
Extract and select characteristics, there are two types: simple and complex. Simple features are a direct measurement of the signal, while complex features are linear or non-linear combinations, ratios, statistics or other transformations of the simple features.
After identifying and estimating the electrical characteristics that describe the neural activity to be studied, neural patterns are recognized with the help of machine learning algorithms.
The field of pattern recognition is related to the automatic discovery of regularities in data through the use of computational algorithms, and the use of these regularities to perform actions, such as classifying data into different categories. Subsequently, depending on the detected class, a predefined action is executed.
Feedback information is presented to the user to notify him about the effect that was triggered as a result of his mental state (sensory, motor, emotional or cognitive) identified by the BCI's system.
Neuralink as a direct link between the brain and everyday technology?
Neuralink is currently developing high-bandwidth brain-machine interfaces to connect humans and computers in a California lab set up that is registered as a medical research company. The ultimate goal of Neuralink is to create brain-computer interfaces that can treat various diseases caused by neurological disorders. Such interfaces have the potential to help people with a wide range of clinical disorders.
Researchers have shown that, with the use of these, patients have been able to control cursors of computers, robotic prostheses and speech synthesizers. This shows its potential use in the medical area to treat patients with disabilities due to neurological disorders.
What is the Link?
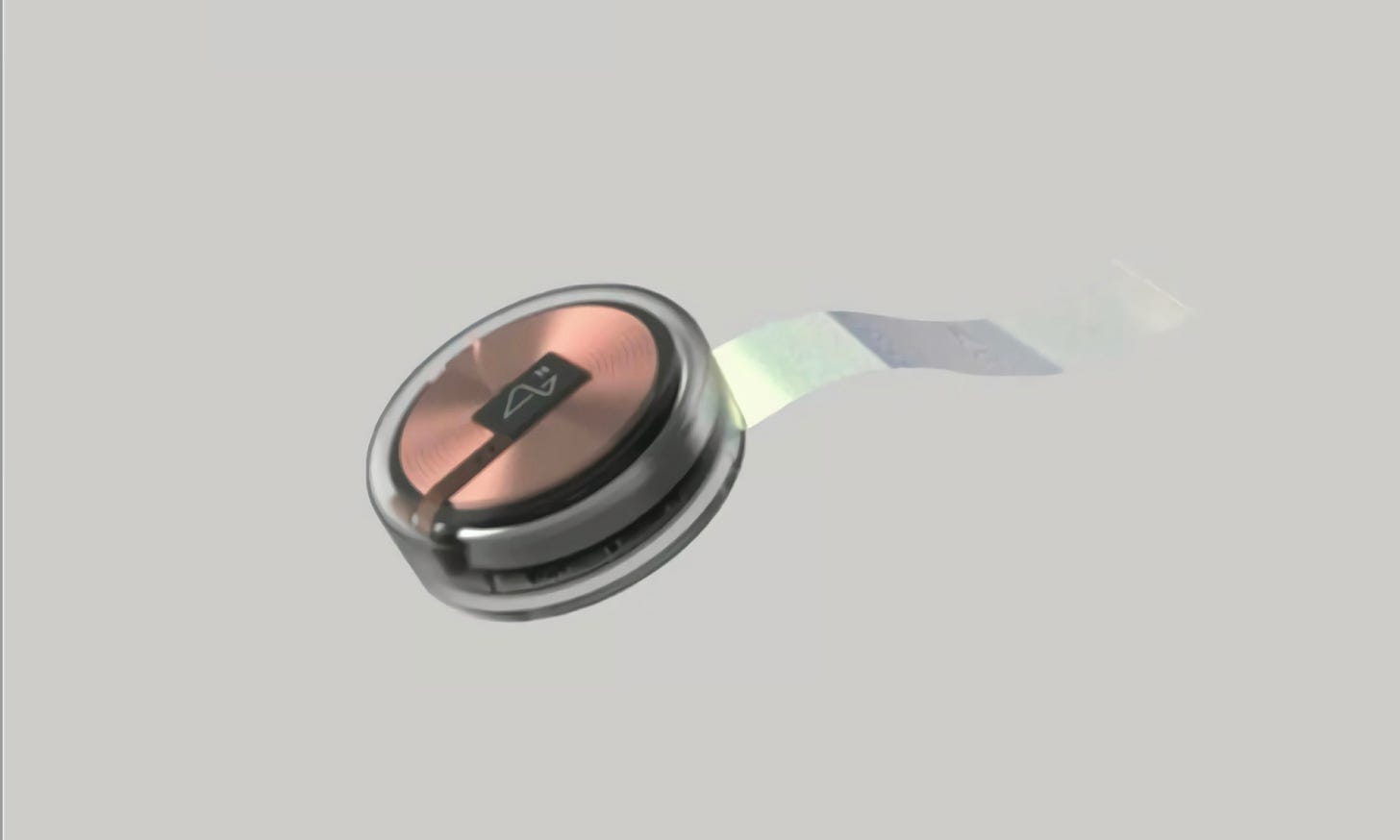
The Neuralink device is called Link and is just 23 x 8 mm. It is implanted directly in the upper cranial cortex. It has multiple sensors, temperature, pressure, six-axis accelerometer, and promises charging for the whole day, with charging by induction when necessary. It’s main function is to record and transmit information in real time from brain neurons to a computer, with its 1,024 electrodes, for interpretation and study.
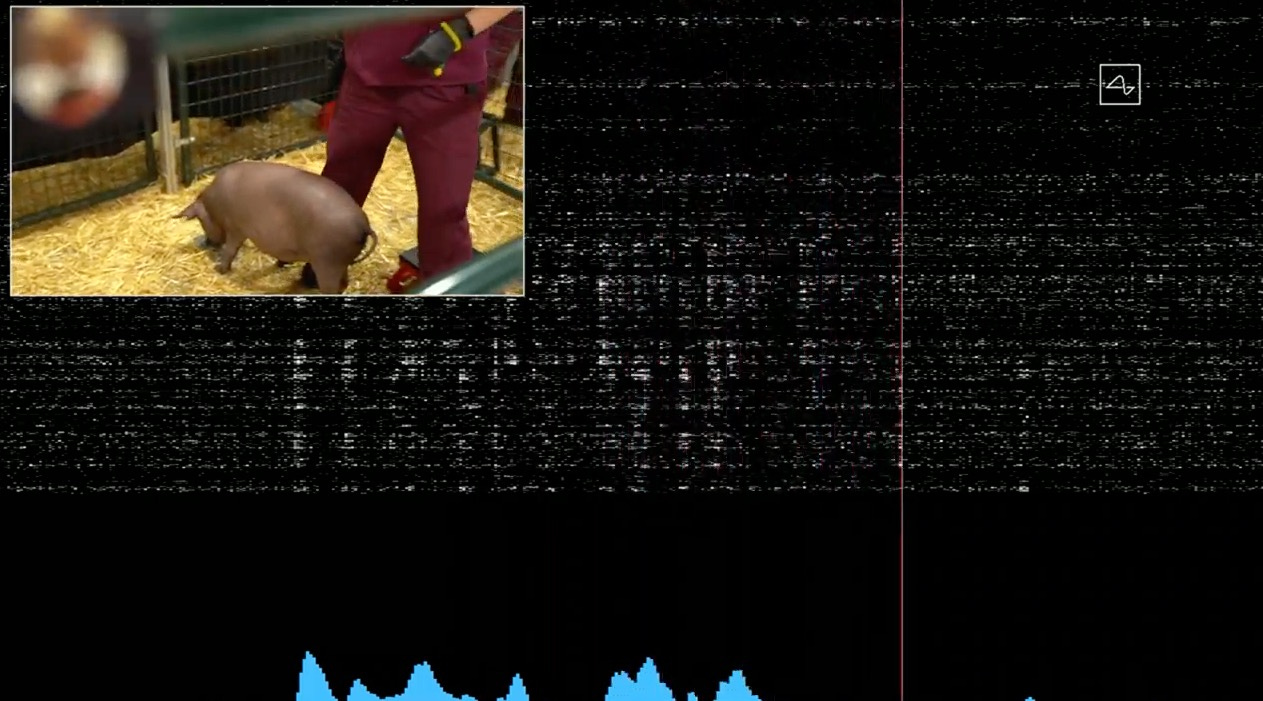
In the presentation where the Link was announced, we could see how Gertrude , a little pig that had the device implanted in the area of her brain linked to her snout. When receiving food, changes in the values were appreciated and we appreciated a sound, this indicated that the neurons were fired.
At the moment it has only been tested in pigs given the similarity with the human brain, although the FDA, the body that controls these devices in the USA, has given the go-ahead for testing in humans.
What is the technology behind the Link?
According to the Neuralink team, the system they are developing will use biocompatible probes that will be inserted into the brain through an automated process performed by a surgical robot. The purpose of these probes is to locate electrical signals in the brain through a series of electrodes connected to them.
The probes are mainly made of polyamide and covered in a thin gold film, both biocompatible materials, so that the chances that the brain considers them as a foreign body, and therefore rejects them, decrease.
Each probe is composed of an area of wires that contains electrodes capable of locating electrical signals in the brain, and a sensory area where the wire interacts with an electronic system that allows the amplification and acquisition of the brain signal. Each probe contains 48 or 96 wires, each with 32 independent electrodes; thus achieving a system of up to 3072 electrodes per formation.
To gain a better understanding of brain function, the Neuralink team announced that it had developed a system capable of converting the electrical signals captured by the electrodes into information represented in binary code. This system is called Application Specific Integrated Circuit.
How will humans interact with the Link?
This is a great question! On April 8 of this year, the businessman and business magnate, Elon Musk, shared with the community on Twitter a video in which Pager, a monkey that has an implanted brain chip, was playing Pong with his mind.
With this technology, Elon Musk assures that will be able to cure affectations of the human body such as blindness, brain damage, addictions and even mentioned that could help patients with severe spinal damage to regain full mobility, with a second implant in the spine.
This type of technology could be calibrated and adapted in the future to allow a person to manage their daily life from their thoughts; sending emails, surfing the internet, listening to music will be activities that we think about and those just happen.
What are the implications and challenges of BCI technologies?
The nonlinear variations of resistive and capacitive transitions between the skin and the surfaces of sensors, solutions for how signals can be further processed after sensing and/or wireless transmission as well as electromagnetic artifacts, are just some important points that still pose considerable challenges.
On the other hand, commonly addressed ethical challenges with BCI technologies concern a future when the technology is used to give people superhuman abilities, or to control their thoughts and desires. Some fear being overtaken by cyborgs with superior cognitive and motoric powers while others are afraid that those would result in mind control, but this will be another topic.
The BCI as such is a recent technology and that a few years ago was seen as unattainable technology, research projects are getting closer, in fact we already see different applications in various branches, although for the moment has its limitations as they are basic tasks, it is also striking as this technology could be helpful in many medical conditions, specifically paraplegic people who have no mobility or sensibility of his body.
References
Am, H a, ley. What is Neuralink? | California Technical Academy [Internet]. [cited 2021 Nov 20]. Available from: https://cta.edu/what-is-neuralink/
Studio P. Home [Internet]. Neuralink. [cited 2021 Nov 20]. Available from: https://neuralink.com/
What is Neuralink? How does Neuralink Work? | by Melville Blogs | Sep, 2021 | Medium [Internet]. [cited 2021 Nov 20]. Available from: https://medium.com/@subhodey080/what-is-neuralink-how-does-neuralink-work-2037607e89f5
Alonso-Valerdi LM, Salido-Ruiz RA, Ramirez-Mendoza RA. Motor imagery based brain–computer interfaces: An emerging technology to rehabilitate motor deficits. Neuropsychologia. 2015 Dec 1;79:354–63.
Deutsche Welle (www. dw.com). Neuralink, de Elon Musk, muestra a un mono con chip cerebral usando videojuego con el pensamiento [Internet]. Www.dw.com. Deutsche Welle (www.dw.com); Available: https://www.dw.com/es/neuralink-de-elon-musk-muestra-a-un-mono-con-chip-cerebral-usando-videojuego-con-el-pensamiento/a-57173399
Dietrich D, Lang R, Bruckner D, Fodor G, Muller B. Limitations, possibilities and implications of Brain-Compxuter Interfaces. En: 3rd International Conference on Human System Interaction. IEEE; 2010
Attiah MA, Farah MJ. Minds, motherboards, and money: futurism and realism in the neuroethics of BCI technologies. Front Syst Neurosci. 2014;8:86



Excellent blog post and I like that it focuses on one particular example of brain-computer interfaces like Neuralink. What was the reason for choosing neuralink as an example of these interfaces? and analyzing the applications. What do you think is the most important factor driving technological development in this area, health or entertainment?
MBG
The post of this week was very impressive. Elon Musk is developing great technology with his companies and Neuralink is not an exception. I think the technology that the Link device promises could be a great revolution in the BCI field.
If you could try this device, would you?